Terms
  |
Machine Authentication
The authorization of an automated human-to-machine or machine-to-machine (M2M) communication through verification of a digital certificate or digital credentials. Unlike user authentication, the process does not involve any action on the part of a human. |
  |
Machine Data
Also known as machine-generated data, this is digital information created by the activity of computers, mobile phones, embedded systems, and other networked devices. |
  |
Machine Learning
A subfield of computer science that evolved from the study of pattern recognition in artificial intelligence. Machine learning is a subfield of computer science that evolved from the study of pattern recognition and computational learning theory in artificial intelligence. |
  |
Machine to Machine
Technologies that allow both wireless and wired devices to communicate and perform actions with other devices of the same type without the assistance of a human. |
  |
Machine Type Communications
Machine Type Communications (MTCI) is a 3rd Generation Partnership Project standard describing machine-to-machine communications. MTC has a wide range of potential applications and is gaining interest among mobile network operators, equipment vendors, specialist companies, and research bodies. |
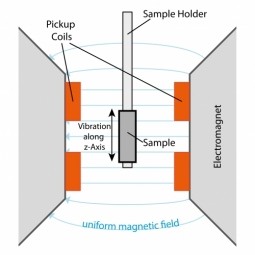  |
Magnetometer
Magnetometers are measurement instruments used for two general purposes: to measure the magnetization of a magnetic material like a ferromagnet, or to measure the strength and, in some cases, the direction of the magnetic field at a point in space. |
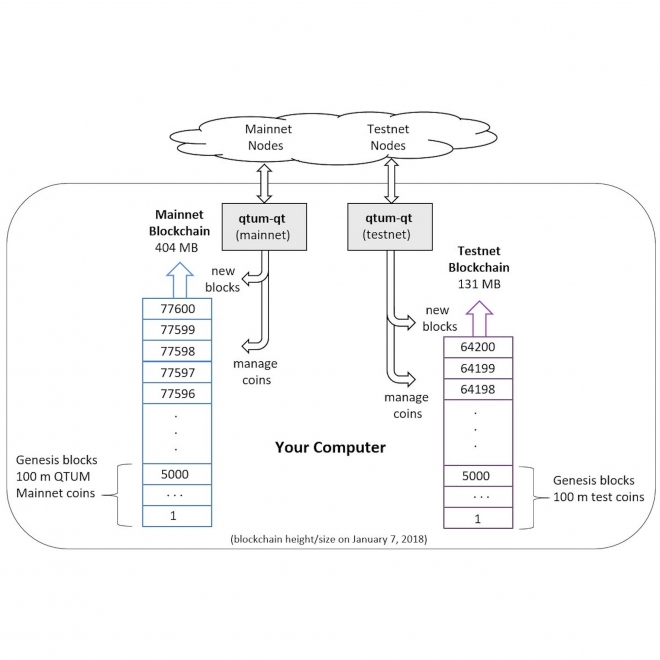 |
Mainnet
A mainnet is a Blockchain that carries out the functionality of transferring digital currency from senders to recipients. This is different from a testnet, which is just a test of such transaction functionality. |
|
Malware
Malware or malicious software is designed to cause damage or disruption to a computer, server, or computer network. A wide variety of types of malware exist, including computer viruses, worms, Trojan horses, ransomware, spyware, adware, and scareware. |
|
|
Man-in-the-middle Attack
In cryptography and computer security, a man-in-the-middle attack is when an attacker intercepts communications between two parties either to secretly eavesdrop or modify traffic traveling between the two. |
|
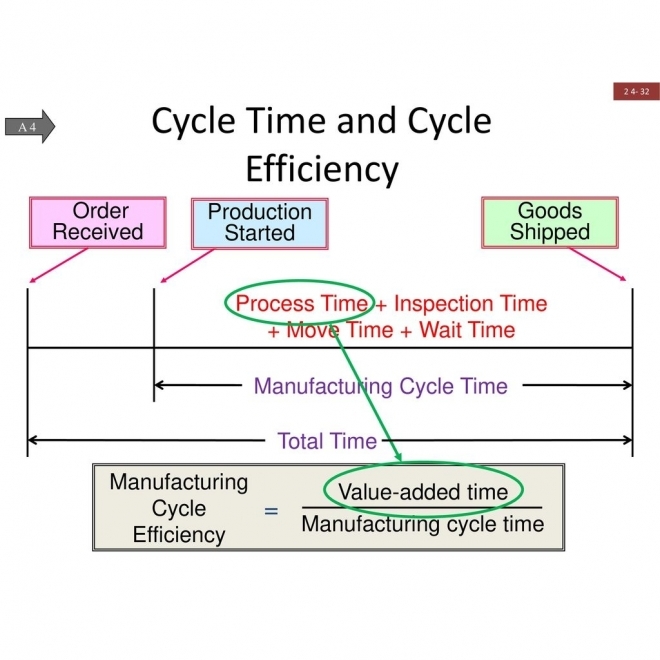  |
Manufacturing Cycle Time
The time of actual production from the moment a customer order arrives on the plant floor to the completion of all product manufacturing, assembly, and testing. |
 |
Markerless AR
Markerless AR is used to denote an Augmented Reality application that does not need any pre-knowledge of a uses environment to overlay 3D content into a scene and hold it to a fixed point in space. |
  |
M-Bus
M-Bus is a European standard covering remote readout of meters and can be used with different types of consumption meters and various types of valves and actuators. |
|
Mechanical Computer Aided Design
Mechanical Computer-aided Design (MCAD) software is used to create and modify geometry, including both 2D and 3D, to order to design, assess and document mechanical components, sheet metal components, assemblies, products, as well as molds, dies, and other toolings. |
|
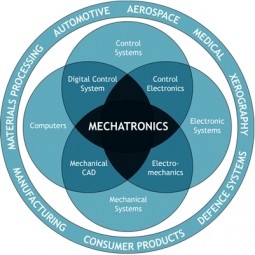  |
Mechatronics
A combination of the words “mechanical” and “electronics,” mechatronics brings together electrical engineering, control engineering, computer engineering, and mechanical engineering disciplines. |
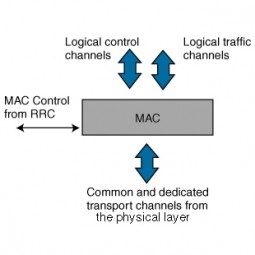  |
Media Access Control
In the IEEE 802 reference model of computer networking, the medium access control or media access control (MAC) layer is the lower sublayer of the data link layer (layer 2) of the seven-layer OSI model. |
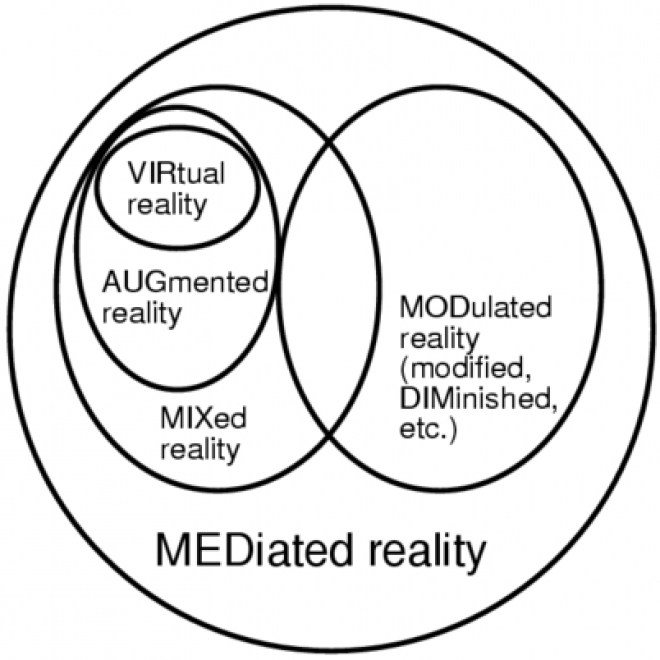 |
Mediated Reality
Mediated Reality is the technological process by which the WearComp user can mediate all visual input and output. Mediation includes overlaying virtual objects on "real life," and taking away or otherwise visually altering objects. |
  |
Mesh Networking
Mesh Networking is an ad-hoc, local area network infrastructure where the nodes communicate directly with each other without the need to pass through a central structure such as an ISP. |
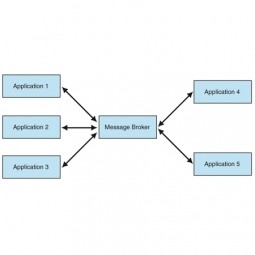  |
Message Broker
A middleware program that translates a message from the messaging protocol of the sender into the messaging protocol of the receiver. Many messaging patterns (like publish-subscribe) can work without a message broker. |
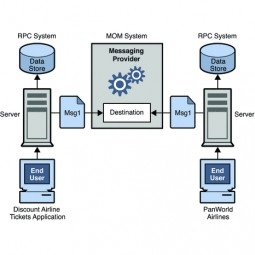  |
Message-Oriented Middleware
Middleware that allows for synchronous as well as asynchronous (queue) messaging between distributed systems. Message-oriented middleware is software or hardware infrastructure supporting the sending and receiving of messages between distributed systems. |
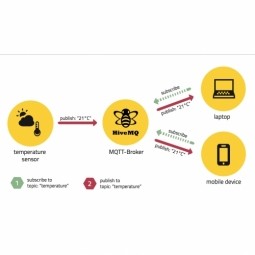  |
Message Queue Telemetry Transport
An open, lightweight M2M communications protocol for the transfer of telemetry messages. MQTT is a publish-subscribe based "light weight" messaging protocol for use on top of the TCP/IP protocol. |
  |
Metasys Platform
A smart building, smart equipment, sensor integration developed by Johnson Controls. The Metasys system is a leading Building Automation System and the foundation of modern building efficiency. |
  |
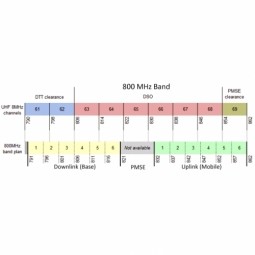
92 MHz
License-free RF band commonly used for short-range applications. 92 MHz low frequency allows for better penetration through walls and obstacles. However, it has a low data transfer rate. |
  |
868 MHz
License-free RF band commonly used for short-range applications such as thermostats, burglar alarms, and industrial uses. It is a part of the spectrum known as "UHF Bands IV and V." |
  |
Microcontroller Unit
A microcontroller (MCU) is a small computer on a single chip. The chip contains a CPU, a clock, non-volatile memory for the program (ROM or flash), volatile memory for input and output (RAM), and an I/O control unit. |
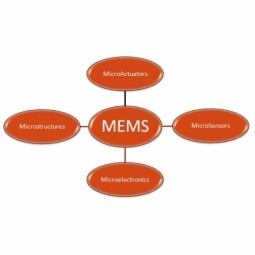  |
Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems
Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) is a miniaturized mechanical and electro-mechanical element typically used for measurements. They usually consist of a central unit that processes data and several components that interact with the surroundings, such as microsensors. |
  |
Microelectronics
The study and manufacture of very small electronic designs and components. Microelectronics is a subfield of electronics. As the name suggests, microelectronics relates to the study and manufacture (or microfabrication) of very small electronic designs and components. |
  |
Microprocessor Unit
A microprocessor is a computer processor that incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit (CPU) on a single integrated circuit (IC), or at most a few integrated circuits. |
|
Microservices
Microservices is a software architecture style. It is based on small building blocks that focus on a single responsibility and function and uses a modular approach to combine large complex applications. |
|
|
Mobile Enterprise Application Platform
An IoT platform designed for use on mobile devices, IOS, Android, Tablets. It utilizes all of the smart features of the modern mobile phone and can add value through communication, collaboration, and ease of use. |
|
  |
Mobile Personal Emergency Response System
Mobile Personal Emergency Response System (MPERS) is a wearable device, such as a pendant, that is connected to a cellular network enabling the user to summon help indoors or outdoors. |
